Recognizing Ebola symptoms like fever, headache, vomiting, and bleeding is crucial. Ignoring Ebola symptoms can be dangerous, so seek immediate care if exposed. Early action saves lives and prevents spread. Stay alert to Ebola symptoms for timely intervention. Early diagnosis improves survival chances and helps contain outbreaks. Always prioritize safety and consult healthcare professionals if you suspect Ebola symptoms.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Ebola is a severe, often fatal viral infection that requires immediate attention. Recognizing early warning signs can make the difference between life and death. This article provides a comprehensive guide on Ebola symptoms, transmission, and prevention strategies.
What is Ebola?
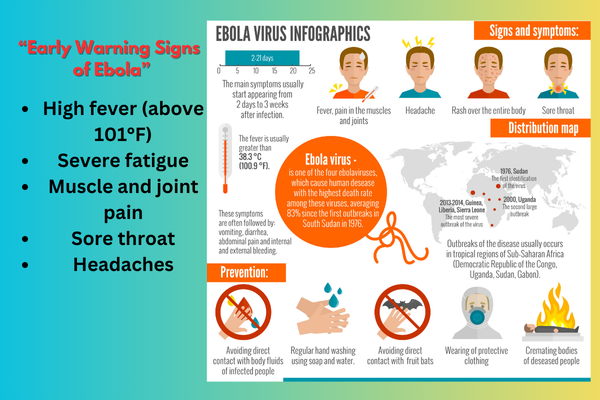
Ebola virus disease (EVD) is caused by viruses from the Filoviridae family. It was first identified in 1976 near the Ebola River in the Democratic Republic of Congo. The virus leads to severe hemorrhagic fever, affecting multiple organs.
How Does Ebola Spread?
Ebola spreads through direct contact with bodily fluids of infected individuals, including blood, saliva, and sweat. The virus can also be transmitted through contaminated surfaces and animal reservoirs, particularly bats and primates.
Early Warning Signs of Ebola
Recognizing early symptoms is crucial. The first signs of Ebola include:
- High fever (above 101°F)
- Severe fatigue
- Muscle and joint pain
- Sore throat
- Headaches
Advanced Symptoms of Ebola
As the disease progresses, more severe symptoms emerge:
- Internal and external bleeding
- Organ failure
- Vomiting and diarrhea
- Difficulty breathing
- Severe dehydration
How Ebola Affects the Body
Ebola attacks the immune system and vital organs. It causes widespread inflammation, leading to multi-organ failure if untreated.
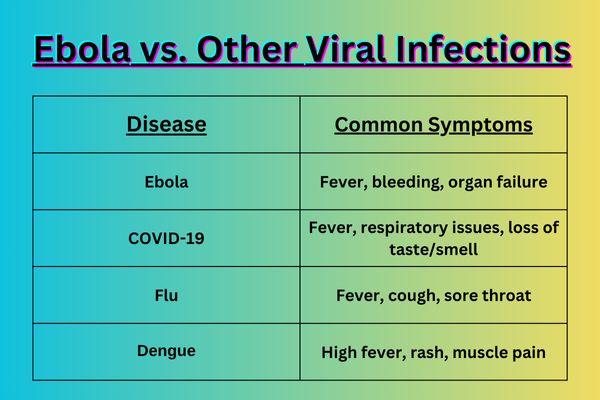
Ebola vs. Other Viral Infections
Ebola shares symptoms with other infections, making diagnosis challenging. Here’s a comparison:
Here, GBS Virus: Causes, Triggers & What You Need to Know
Who is at Risk?
Certain groups are more vulnerable to Ebola, including:
- Healthcare workers
- Family members of infected patients
- People living in outbreak regions
How to Prevent Ebola?
Preventative measures include:
- Vaccination: The rVSV-ZEBOV vaccine is effective against Ebola.
- Hygiene Practices: Frequent handwashing and avoiding direct contact with infected individuals.
- Safe Burial Practices: Handling deceased patients with extreme caution.
Diagnosis and Testing for Ebola
Ebola diagnosis involves:
- PCR Tests: Detects viral RNA in blood samples.
- Serology Tests: Identifies antibodies in recovered patients.
Current Treatments for Ebola
While no universal cure exists, supportive care improves survival rates. Treatments include:
- Monoclonal Antibodies: Such as Inmazeb (atoltivimab, maftivimab, odesivimab).
- Fluid Replacement Therapy: Prevents dehydration and shock.
Survival Rate and Recovery
Ebola has a high fatality rate, but early intervention increases survival chances. Recovery involves long-term monitoring for post-Ebola syndrome.
Ebola Outbreaks and Global Response
Notable outbreaks include the 2014 West Africa outbreak and the 2018 DRC outbreak. Global efforts by WHO and CDC continue to improve response strategies.
Common Myths About Ebola
- Myth: Ebola spreads through air.
- Fact: Ebola requires direct contact for transmission.
- Myth: Only Africa is affected.
- Fact: Imported cases have occurred worldwide.
FAQs
1. What are the first symptoms of Ebola?
Early symptoms include fever, fatigue, and muscle pain.
2. How long does it take for Ebola symptoms to appear?
Symptoms develop within 2-21 days after exposure.
3. Can you recover from Ebola?
Yes, with early treatment, many patients survive and recover fully.
4. Is there a vaccine for Ebola?
Yes, the rVSV-ZEBOV vaccine provides effective protection.
5. How is Ebola different from COVID-19?
Ebola causes internal bleeding, while COVID-19 primarily affects the respiratory system.
6. Can animals transmit Ebola to humans?
Yes, bats and primates are natural reservoirs of the virus.
Conclusion
Ebola is a deadly disease, but recognizing symptoms early can save lives. Prevention, vaccination, and awareness play key roles in controlling outbreaks. Stay informed and practice caution to reduce risks.